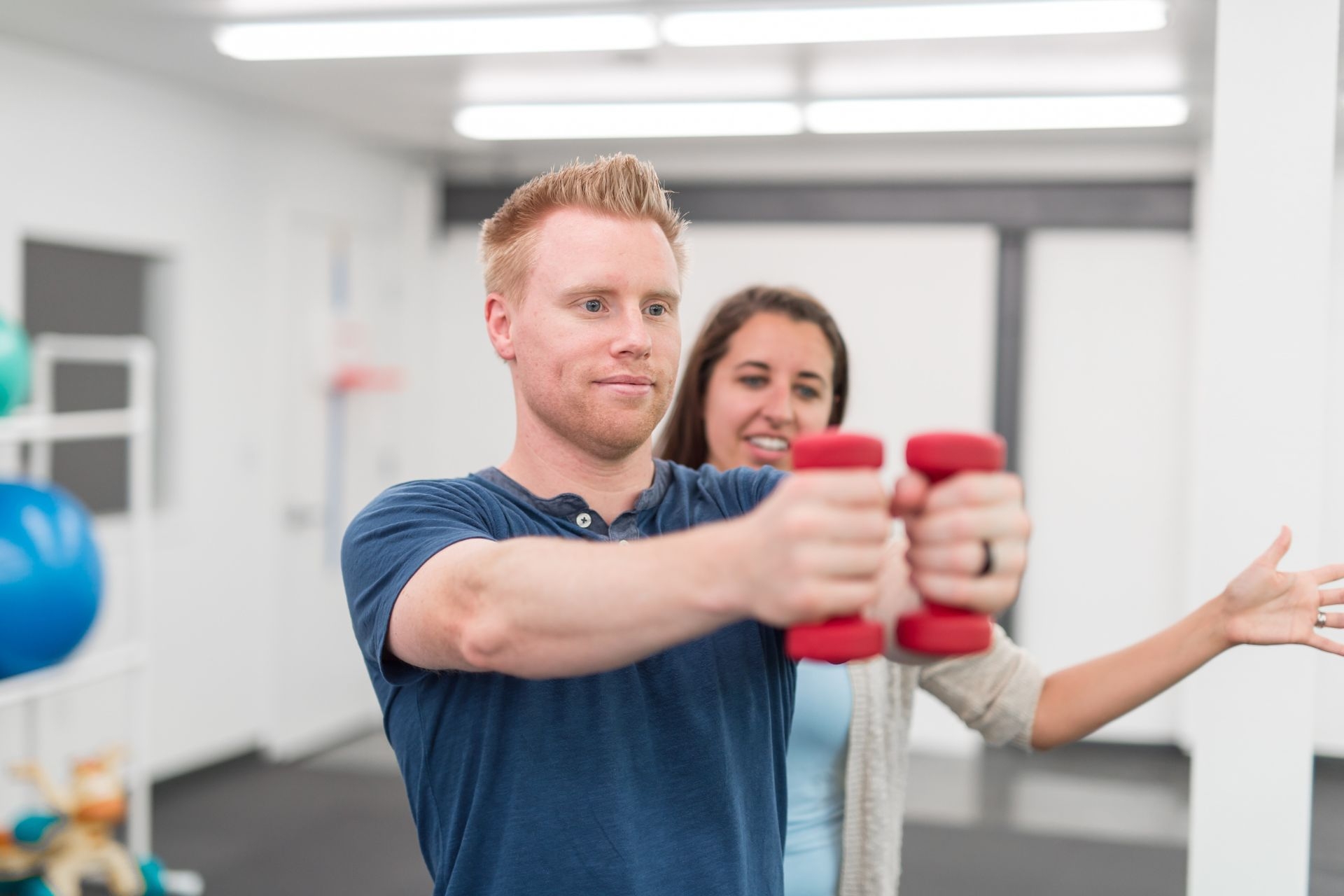


Postural assessment is the evaluation of an individual's body alignment and positioning in order to identify any deviations or imbalances. Feldenkrais Method It involves observing the alignment of the head, shoulders, spine, pelvis, and lower extremities, as well as assessing the individual's movement patterns. Postural assessment is important because it can help identify any postural abnormalities or imbalances that may contribute to musculoskeletal issues or pain. By identifying these issues early on, appropriate interventions can be implemented to prevent further complications and improve overall musculoskeletal health.
Poor posture can manifest in various signs and symptoms. Common signs include rounded shoulders, forward head posture, hunched back, and an exaggerated curve in the lower back. Individuals with poor posture may also experience muscle imbalances, such as tightness in certain muscles and weakness in others. Myofascial Release This can lead to discomfort, pain, and limited range of motion. Additionally, poor posture can contribute to headaches, fatigue, and decreased overall function.
Poor posture can have a significant impact on the musculoskeletal system. It can lead to muscle imbalances, as certain muscles become overused and others become weakened. Exercise Therapy This can result in joint dysfunction, as the imbalances can affect the alignment and movement of the joints. Over time, this can lead to increased wear and tear on the joints, potentially leading to conditions such as osteoarthritis. Poor posture can also put excessive stress on the ligaments, tendons, and discs of the spine, increasing the risk of injury and degenerative changes.
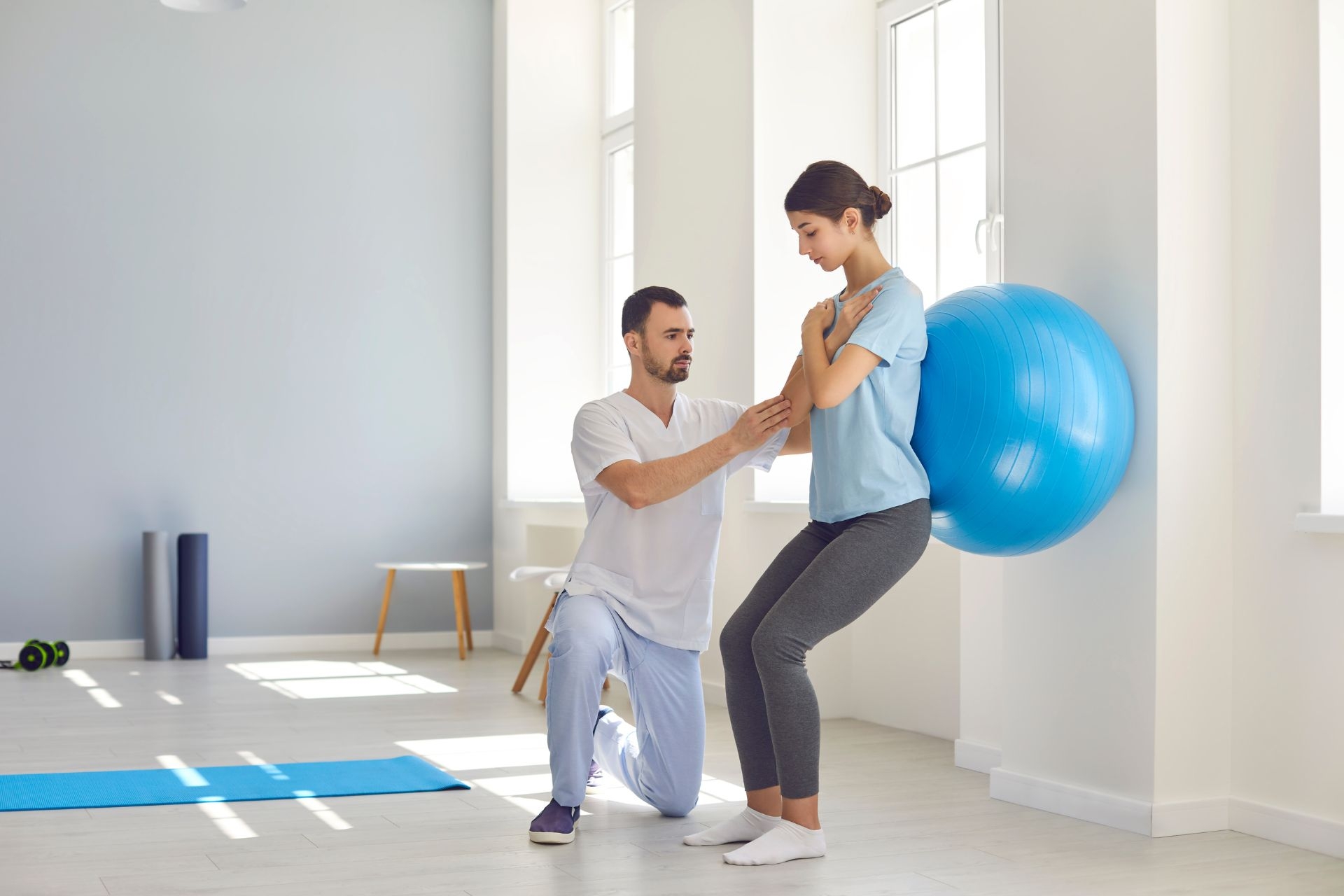

Untreated postural issues can have long-term effects on an individual's musculoskeletal health. Chronic poor posture can lead to the development of structural abnormalities, such as scoliosis or kyphosis. It can also contribute to the progression of degenerative conditions, such as osteoarthritis. Additionally, poor posture can increase the risk of musculoskeletal injuries, as the imbalances and misalignments can put excessive stress on the joints and soft tissues. Adaptive Equipment Over time, this can lead to chronic pain, decreased mobility, and decreased quality of life.
There are several common causes of poor posture. Sedentary lifestyles, where individuals spend prolonged periods sitting or slouching, can contribute to the development of poor posture. Weak core muscles and poor muscle flexibility can also contribute to postural imbalances. Additionally, factors such as improper ergonomics, improper lifting techniques, and excessive weight can all contribute to poor posture. Trigger Point Therapy It is important to address these underlying causes in order to effectively improve posture and prevent further complications.
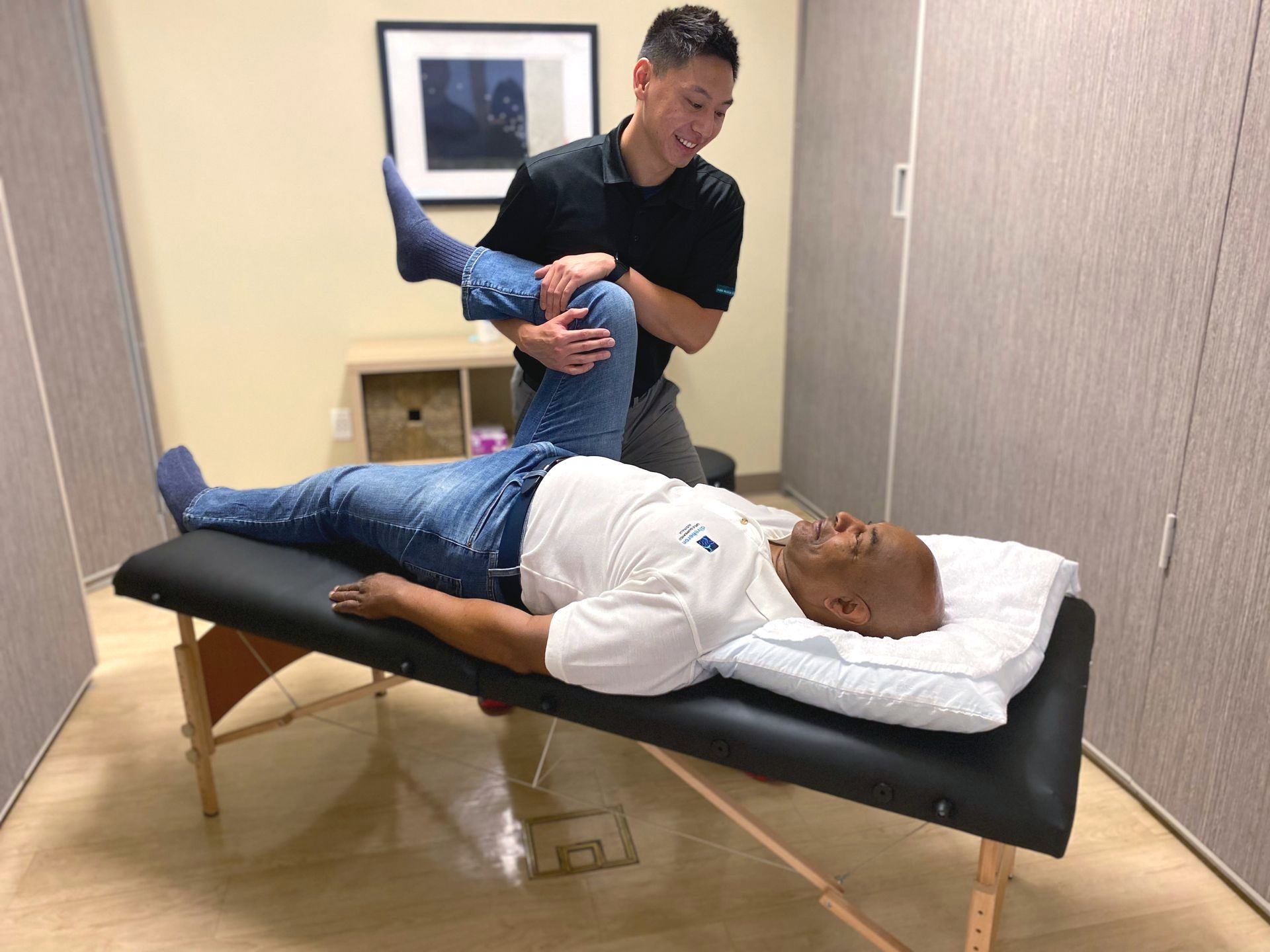
Postural assessment can be a valuable tool in preventing and managing musculoskeletal injuries. By identifying postural imbalances and deviations early on, appropriate interventions can be implemented to correct these issues. This may include exercises to strengthen weak muscles, stretches to improve flexibility, and ergonomic modifications to improve alignment during daily activities. By addressing these issues proactively, individuals can reduce their risk of developing musculoskeletal injuries and improve their overall musculoskeletal health.
There are several effective strategies for improving posture and maintaining good alignment. Regular exercise, particularly exercises that target the core muscles and promote flexibility, can help strengthen the muscles that support proper posture. Practicing good ergonomics, such as maintaining proper sitting and standing posture, can also help improve alignment. Additionally, taking frequent breaks from prolonged sitting or standing, and incorporating regular stretching and movement breaks, can help prevent postural imbalances. It is also important to be mindful of body mechanics during daily activities, such as lifting heavy objects, in order to maintain good alignment and prevent injury.

Physical therapy is a highly effective treatment approach for addressing rotator cuff injuries. The primary goal of physical therapy is to reduce pain, improve range of motion, and restore strength and function to the affected shoulder. Physical therapists use a variety of techniques and exercises to achieve these goals. These may include manual therapy techniques such as joint mobilizations and soft tissue mobilizations, as well as therapeutic exercises to strengthen the rotator cuff muscles and surrounding shoulder muscles. Additionally, physical therapists may incorporate modalities such as ultrasound or electrical stimulation to help reduce pain and inflammation. Through a comprehensive and individualized treatment plan, physical therapy can help patients recover from rotator cuff injuries and regain optimal shoulder function.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing ankylosing spondylitis, a chronic inflammatory disease that primarily affects the spine. The goal of physical therapy is to improve mobility, reduce pain, and enhance overall function. Physical therapists use a variety of techniques, including exercises, stretches, and manual therapy, to address the specific needs of individuals with ankylosing spondylitis. These interventions aim to increase flexibility, strengthen muscles, and improve posture, which can help alleviate symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease. Additionally, physical therapists may provide education on proper body mechanics and ergonomics to prevent further damage to the spine. By working closely with physical therapists, individuals with ankylosing spondylitis can optimize their physical well-being and maintain an active and fulfilling lifestyle.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the treatment of hip impingement, also known as femoroacetabular impingement (FAI). FAI occurs when there is abnormal contact between the femoral head and the acetabulum, leading to pain and limited range of motion in the hip joint. Physical therapy aims to address these symptoms and improve overall hip function through a variety of interventions. These may include therapeutic exercises to strengthen the muscles around the hip joint, such as the glutes and hip flexors, to provide better support and stability. Manual therapy techniques, such as joint mobilizations and soft tissue mobilizations, can help reduce pain and improve joint mobility. Additionally, physical therapists may use modalities like heat or ice therapy to manage pain and inflammation. Education on proper body mechanics and movement patterns is also an important aspect of physical therapy for FAI, as it helps individuals avoid activities that may exacerbate their symptoms. Overall, physical therapy plays a vital role in the comprehensive management of hip impingement, helping individuals regain function, reduce pain, and improve their quality of life.
Physical therapy is a highly effective treatment option for individuals suffering from sacroiliac joint dysfunction. By utilizing a combination of targeted exercises, manual therapy techniques, and modalities, physical therapists can help alleviate pain, improve joint stability, and restore normal function to the sacroiliac joint. Through exercises that focus on strengthening the surrounding muscles, such as the glutes and core, physical therapy can help stabilize the joint and reduce stress on the sacroiliac ligaments. Additionally, manual therapy techniques, such as joint mobilizations and soft tissue mobilizations, can help improve joint mobility and reduce pain. Overall, physical therapy plays a crucial role in the management of sacroiliac joint dysfunction, providing patients with a comprehensive and personalized treatment plan to address their specific needs.
Manual therapy in physical therapy refers to a hands-on approach used by physical therapists to diagnose and treat musculoskeletal conditions. It involves the skilled manipulation and mobilization of joints, soft tissues, and muscles to improve range of motion, reduce pain, and enhance overall function. Manual therapy techniques may include joint mobilization, soft tissue mobilization, myofascial release, trigger point therapy, and stretching. These techniques are performed by the physical therapist using their hands or specialized tools to apply pressure, traction, or movement to the affected area. Manual therapy is often used in conjunction with other therapeutic modalities and exercises to optimize the outcomes of physical therapy treatment.
Physical therapy can be an effective treatment option for managing muscular atrophy. By utilizing targeted exercises and techniques, physical therapists can help individuals with muscular atrophy improve muscle strength, flexibility, and overall function. These exercises may include resistance training, stretching, and range of motion exercises, all of which can help to stimulate muscle growth and prevent further muscle wasting. Additionally, physical therapists can provide education on proper body mechanics and posture, as well as assistive devices and adaptive equipment, to help individuals with muscular atrophy maintain independence and improve their quality of life. Overall, physical therapy plays a crucial role in the management of muscular atrophy by addressing the specific needs and goals of each individual and providing a comprehensive approach to rehabilitation.
Blood flow restriction therapy, also known as BFR therapy, is a specialized technique used in physical therapy to enhance muscle strength and promote muscle growth. It involves the application of a specialized cuff or band around the limb, which is then inflated to partially restrict blood flow to the working muscles. This technique allows for the muscles to be trained at a lower intensity while still achieving the same benefits as high-intensity exercise. BFR therapy has been shown to increase muscle protein synthesis, improve muscle endurance, and enhance overall muscle function. It is often used in rehabilitation settings to help patients recover from injuries or surgeries, as well as in sports performance training to optimize muscle development.